Introduction to PBM
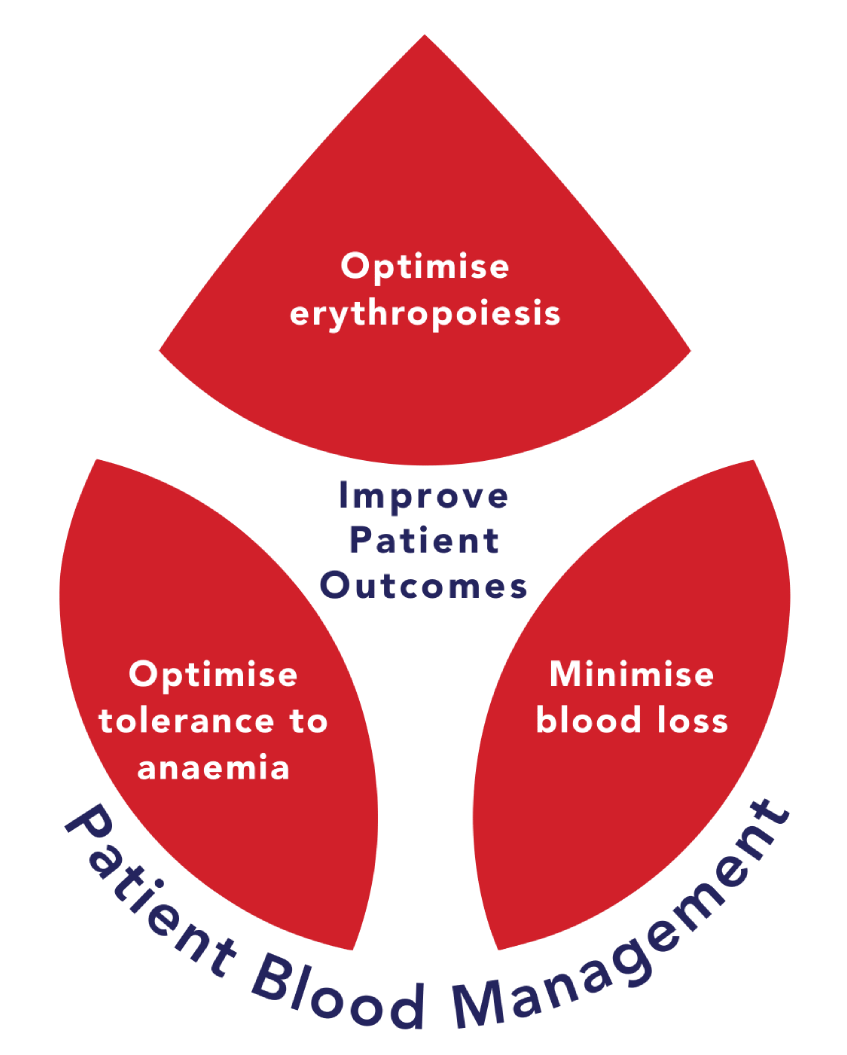
Patient Blood Management (PBM) is the scientific use of safe, effective medical and surgical techniques to prevent anaemia and reduce blood loss. PBM focusses on the patient and in optimising patient outcomes. It primarily looks at the health of blood peri-operatively, in chronic illnesses, heavy menstrual bleeding and also during pregnancy. Optimising patient blood health and minimising blood loss in these settings is the key to ensuring good patient outcome.
PBM is a multidisciplinary approach through educating practitioners,researching latest surgical techniques and educating the patient in best options for blood management. A large body of evidence shows that anaemia, blood loss, and transfusion are independent risk factors for adverse outcomes in surgery including morbidity, mortality and average length of hospital stay (4–7 days). PBM is a concept to reduce and pre-empt the detrimental impact of this triad. PBM is an evidence-based bundle of care to optimise medical and surgical patient outcomes by clinically managing and preserving a patient's own blood.
PBM is centred around three pillars; optimise haemostasis, minimise blood loss and bleeding and harness and optimise tolerance of anaemia. Using these foundations Peri-Operatively (Preoperative, Intraoperative and Postoperative) is essential to working with patients and optimising their blood health and outcomes.
Patients on wait lists for surgery should take action to ensure they are as fit as possible. This will help achieve the best outcomes from the surgery and help in recovery. Getting a patient fit for surgery means assessing their risks of complications and treating any that can be treated.
Hofman et al., 2020, Research Quare, Call to Action – Closing the Gap to Make Patient Blood Management the New Norm(al) as. Viewed by Implementors in Diverse Countries.
Find Out More